KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 1.3 are part of KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions. Here we have given Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Arithmetic Progressions Exercise 1.3.
Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Arithmetic Progressions Exercise 1.3
Question 1.
FInd the sum of the following APs:
i) 2, 7, 12, ……… to 10 terms
ii) -37, -33, -29,………. to 12 terms.
iii) 0.8, 1.7, 2.8 to 100 terms.
iv) \(\frac{1}{15}, \frac{1}{12}, \frac{1}{10} \ldots, \text { to } 11\) terms
Solution:
i) Sum of 2, 7, 12, ………. 10?
a = 2, d = 7 – 2 = 5, n = 10
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(s_{10}=\frac{10}{2}[2 \times 2+(10-1) 5]\)
= 5[4 + 9 × 5]
= 5[4 + 45]
= 5 × 49
∴ S10 = 245
ii) -37, -33, -29, to 12……. terms.
Solution:
a = -37, d = -33 – (-37) = -33 + 37
n = 12, d = 4
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{12}=\frac{12}{2}[2 \times -37+(12-1) 4]\)
= 6[-74 + 11 × 4]
= 6[-74 + 44]
= 6 × -30
∴ S12 = -180.
iii) 0.6, 1.7, 2.8,……… , to 100 terms.
a = 0.6, d = 1.7 – 0.6 = 1.1
n = 100, S100 =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{100}=\frac{100}{2}[2 \times 0.6+(100-1)(1.1)]\)
= 50[1.2 + 99(1.1)]
= 50[1.2 + 108.9]
= 50 × 110.1
∴ S100 = 5505
iv) \(\frac{1}{15}, \frac{1}{12}, \frac{1}{10} \ldots, \text { to } 11\) terms
Solution:

The LCM of 12 and 18 is 36.
Question 2.
Find the sums given below:
i) \(7+10 \frac{1}{2}+14+\ldots \ldots+84\)
ii) 34 + 32 + 30 + ……….+ 10
iii) -5 + (-8) + (-11) + ……….. +(-230)
Solution:
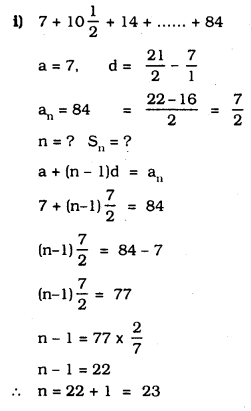

ii) 34 + 32 + 30 + ………. + 10
Solution:
a = 34, d = 32 – 34 =-2, an = 10,
Sn =?
a + (n – 1)d = an
34 + (n – 1)(-2) = 10
34 – 2n + 2 = 10
-2n + 36 = 10
-2n = 10 – 36
-2n = -26
2n = 26
\(n=\frac{26}{2}\)
∴ n = 13
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[a+l]\)
\(\mathrm{S}_{23}=\frac{13}{2}[34+10]\)
\(=\frac{13}{2} \times 44\)
= 13 × 22
∴ S23 = 286.
iii) -5 + (-8) + (-11) +……… + (-230)
Solution:
a = -5, d = -8 – (-5) = -8 + 5
a, = -230.
Sn =? d = -3
a+(n – 1)d = an
-5 + (n – 1)(-3) = -230
-5 – 3n + 3 = -230
-3n – 2 = -230
-3n = -230 +2
-3n = -228
3n = 228
∴ n = 228/3
∴ n = 76.
\(\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{n}}=\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}\left[\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{n}}\right]\)
\(S_{ 76 }=\frac { 76 }{ 2 } \left[ -5-230 \right] \)
\(=\frac{76}{2} \times -235\)
= 38 × -235
∴ S76= -8930.
Question 3.
In an AP:
i) given a = 5. d = 3. an = 50, find ‘n’ and Sn.
ii) given a = 7, a13 = 35, find d’ and S13.
iii) given a12= 37. d = 3. find ‘a’ and S12.
iv) given a3 = 15, S10 = 125. find ‘d’ and a10.
v) given d = 5. S9 = 72, fInd ‘a’ and a9.
vi) given a = 2. d = 8, Sn = 90, fInd ‘n and a11.
vii) given a = 8, an = 62. Sn = 210, find ‘n’ and ‘d’.
viii) given an = 4, d = 2, Sn = -14. find ‘n’ and a.
ix) given a = 3, n = 8, S = 192, find ‘d’.
x) given L = 28, S = 144 and there are total 9 terms. Find ‘a’.
Solution:
i) a = 5, d = 3, an = 50. n=?, Sn =?
a + (n – 1)d = an
5 + (n – 1) 3 = 50
5 + 3n – 3 = 50
3n + 2 = 50
3n = +50 – 2
3n = 48
\(n=\frac{48}{3}\)
∴ n = 16
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}\left[a+a_{n}\right]\)
\(S_{16}=\frac{16}{2}[5+50]\)
\(=\frac{16}{2}[55]\)
= 8 × 55
∴ S16= 440.
ii) a = 7, a13 = 35. d =?. S13 =?
Solution:
a+(n – 1) d = an
7 + (13 – 1) d = 35
7 + 12d = 35
12d = 35 – 7
12d = 28
\(d=\frac{28}{12}\)
\(d=\frac{7}{3}\)
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}\left[a+a_{n}\right]\)
\(S_{n}=\frac{7}{3} \times \frac{1}{2}[7+35]\)
\(\mathrm{s}_{\mathrm{n}}=\frac{7}{6} \mathrm{I} 42 \mathrm{l}\)
= 7 × 7
∴ Sn = 49
iii) a12= 37, d = 3, a =? S12 =?
a + (n – 1)d = an
a + (12 -1) 3 = 37
a + 11 × 3 = 37
a + 33 = 37
∴ a = 37 – 33
∴ a = 4
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}\left[a+a_{n}\right]\)
\(\mathrm{S}_{12}=\frac{12}{2}[4+37]\)
= 6[4 + 37]
∴ S2 = 246
iv) a3 = 15, S10 = 125. d =?, a10=?
Solution:
a3 = a + 2d = 15
∴ a= 15 – 2d
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(s_{10}=\frac{10}{2}[2(15-2 d) \div(10-1) d]=125\)
= 5[30 – 4d + 9d] = 125
= 5[30 + 5d] = 125
150 + 25d = 125
25d = 125 + 150
25d = -25
\(\mathrm{d}=\frac{-25}{25}\)
∴ d = -1.
Substittuting the value of ‘d’
a = 15 – 2d
= 15 – 2(-1)
= 15 + 2
∴ a = 17.
∴ a10 = a + 9d
= 17 + 9(-1)
= 17 – 9
∴ a10 = 8
v) d = 5, S9 = 72. a =? a9 =?
Solution:
\(\mathrm{s}_{\mathrm{n}}=\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}[2 \mathrm{a}+(\mathrm{n}-1) \mathrm{d}]\)
\(s_{9}=\frac{9}{2}[2 \times a+(9-1) 5]=72\)
\(\frac{9}{2}[2 a+8 \times 5]=72\)
\(\frac{9}{2}[2 a+40]=72\)
\(2 a+40=72 \times \frac{2}{9}\)
2a + 40 = 16
2a = 16 – 40
2a = -24
\(a=\frac{-24}{2}\)
∴ a = -12
a9 = a + (n – 1) d
= -12 + (9 – 1) (5)
= -12 + 8 × 5
= -12 + 40
∴ a9 = 28
vi) a = 2, d = 8 Sn = 90, n =?, a3 =?
Solution:
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(=\frac{n}{2}[2 \times 2+(n-1) 8]=90\)
\(\frac{n}{2}[4+8 n-8]=90\)
n (8n – 4) = 90 × 2/1
8n2 – 4n = 180
8n2 – 4n = 1800
2n2 – n – 45 = 0

2n2– 10n + 9n – 45 = 0
2n(n – 5) + 9(n – 5) = 0
(n – 5)(2n + 9) = 0
If n – 5 = 0 then n = 5
∴ an = a + (n – 1) d
a5= 2 + (5 – 1) 8
= 2 + 4 × 8
= 2 + 32
∴ a5 = 34
vii) a = 8, an = 62, Sn = 210, n =? d =?
Solution:
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}\left[a+a_{n}\right]=210\)
\(\frac{n}{2}[8+62]=210\)
\(\frac{n}{2} \times 70=21\)
\(n=210 \times \frac{2}{70}\)
∴ n = 6
an = 62
a6= a + 5d = 62
8 + 5d = 62
5d = 62 – 8
5d = 54
\(d=\frac{54}{5}\)
viii) a = 4, d = 2, Sn = -14, n =?, a =?
Solution:
an = a + (n – 1) d = 4
a + (n – 1) 2 = 4
a + 2n – 2 = 4
a + 2n = 4 + 2
a = 2n = 6 …………. (i)
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}\left[a+a_{n}\right]=210\)
\(\frac{n}{2}[-2 n+6+4]=-14\)
\(\frac{n}{2}[-2 n+10]=-14\)
-2n2 + 10n = -28
-2n2 + 10n + 28 = 0
2n2 – 10n – 28 = 0 – 14
2n2 – 5n – 14 = 0

n2 – 7n + 2n – 14 = 0
n(n – 7) + 2 (n – 7) = 0
(n – 7) (n + 2) = 0
If n – 7 = 0 then. n = 7
a = -2n + 6
= -2 × 7 + 6
= -14 + 6
∴ a = -8
∴ n = 7, a = -8.
ix) a = 3, n = 8, S = 192, d =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{8}=\frac{8}{2}[2 \times 3+(8-1) d]=192\)
\(\frac { 8 }{ 2 } [6+7\times d]=192\)
4 (6 + 7d) = 192
\(6+7 d=\frac{192}{4}\)
6 + 7d = 48
7d = 48 – 6
7d = 42
\(d=\frac{42}{7}\)
∴ d = 6
x) l = an = 28, S = 144, n = 9, a =?
Solution:
\(s_{n}=\frac{n}{2}\left[a+a_{n}\right]\)
\(s_{9}=\frac{9}{2}[a+28]=144\)
\(\frac{9}{2}[a+28]=144\)
\(a+28=144 \times \frac{2}{9}\)
a + 28 = 32
a = 32 – 28
∴ a = 4.
Question 4.
How many terms of the AP: 9, 17, 25, … must be taken to give a sum of 636?
Solution:
9 + 17 + 25 + ……. + an = 636
a = 9, d = 17 – 9 = 8, Sn= 636, n =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 \times 9+(n-1) 8]=636\)
\(\frac{n}{2}[18+8 n-8]=636\)
\(\frac{n}{2}[8 n+10]=636\)
n(8n + 10) = 636 × 2
8n2 + 10n = 1272
8n2+ 10n – 1272 = 0
4n2 + 5n – 636 = o
4n2+ 5n – 48n – 636 = 0

n(4n + 5) – 12(4n + 5) = 0
(4n + 5) (n – 12) = 0
1f n – 12 = 0 then, n = 12
∴ n = 12.
Question 5.
The first term of an AP is 5. the last term is 45 and the sum is 400. Find the number of terms and the common difference.
Solution:
a = 5, an = 45, Sn= 400, n =?, d =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}\left[a+a_{n}\right]\)
\(=\frac{n}{2}[5+45]=400\)
\(\frac{n}{2} \times 50=400\)
n × 50 = 800
\(n=800 \times \frac{1}{50}\)
∴ n = 16
an = a + (n – 1) d
a16= 5 + (16 – 1)d = 45
5 + 15d = 45
15d = 45 – 5
15d = 40
\(d=\frac{40}{15}=\frac{8}{3}\)
\(\mathrm{n}=16, \mathrm{d}=\frac{8}{3}\)
Question 6.
The first and the last terms of an AP are 17 and 350 respectively. If the common difference is 9, how many terms are there and what is their sum?
Solution:
a = 17, an= 350, d = 9, n =?, Sn =?
an = a + (n – 1) d
17 + (n – 1)9 = 350
17 + 9n – 9 = 350
9n + 8 = 350
9n = 350 – 8
9n = 342
\(\quad n=\frac{342}{9}\)
∴ n = 38
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}\left[a+a_{n}\right]\)
\(S_{38}=\frac{38}{2}[17+350]\)
= 19 × 367
∴ S38 = 6973
∴ n = 38, S38 = 6973
Question 7.
Find the sum of first 22 terms of an AP in which d = 7 and 22nd term is 149.
Solution:
d = 7, a22 = 149, S22 =?
a = a + (n – 1)d
a + (22 – 1)7 = 149
a + 21 × 7 = 149
a + 147 = 149
=149 – 147
∴ a = 2
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}\left[a+a_{n}\right]\)
\(S_{22}=\frac{22}{2}[2+149]\)
= 11[151]
∴ S22 = 1661
Question 8.
Find the sum of first 51 terms of an AP whose second and third terms are 14 and 18 respectively.
Solution:
If a2 = 14, a3 = 18, then S11 =?
a2 = 14
a + d = 14 …………. (i)
a3 = 18
a + 2d = 18 …………… (ii)
from equation (1) – equatIon (11),

d =4.
Substituting the value of ‘d’ In eqn. (i)
a + d = 14
a + 4 = 14
a = 14 – 4
∴ a = 10
a = 10, d = 4
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{51}=\frac{51}{2}[2 \times 10+(51-1) 4]\)
\(=\frac{51}{2}[20+50 \times 4]\)
\(=\frac{51}{2}[20+200]\)
\(=\frac{51}{2} \times 220\)
= 51 × 110
∴ S51 = 5610
Question 9.
If the sum of first 7 terms of an AP is 49 and that of 17 terms is 289, find the sum of first ‘n terms.
Solution:
S7 = 49, S17 = 289, S11 =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{7}=\frac{7}{2}[2 a+(7-1) d]\)
\(=\frac{7}{2}[2 a+6 d]=49\)
[latex2+6 d=49 \times \frac{2}{7}[/latex]
2a + 6d = 14 …………… (i)
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{17}=\frac{17}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(=\frac{17}{2}[2 \mathrm{a}+16 \mathrm{d}]\)
\(\frac{17}{2}[2 a+16 d]=289\)
\(2 a+16 d=289 \times \frac{2}{17}\)
∴ 2a + 16d = 34 …………. (ii)

10d = 20
∴ d=2
Substituting the value of d in equation (i), we have
2a + 6d = 14
2a + 6 × 2 = 14
2a + 12 = 14
2a = 14 – 12
2a = 2
\(a=\frac{2}{2}=1\)
a = 1, d = 2, Sn =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 \times 1+(n-1) 2]\)
\(=\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}[2+2 \mathrm{n}-2]\)
\(=\quad \frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}[2 \mathrm{n}]\)
∴ Sn = n2
Question 10.
Show that a1, a2, a3, … a11. … form an AP where a11 is defIned as below:
i) a = 3 + 4n
ii) a = 9 – 5n
Solution:
i) an= 3 + 4n
a1 = 3 + 4(1)
= 3 + 4
∴ an = 7
∴ a = 7
a1 = 3 + 4n
a2 = 3 + 4 × 2
= 3 + 8
∴ a2 = 11
an = 3 + 4n
a3 = 3 + 4 × 3
= 3 + 12
a3 = 15
∴ a1, a2, a3, ………….
7, 11, 15, ……….
d = a2 – a1 = 11 – 7 = 4
d = a3 – a2= 15 – 11 = 4
Here, the value of ‘d’ is constant.
∴ an = 3 + 4n forms an Arithmetic Progression.
ii) an = 9 – 5n
a1= 9 – 5 × 1
= 9 – 5
∴ a1 = 4
a1 = 9 – 5n
a1 = 9 – 5 × 2
= 9 – 10
∴ a2 = -1
an= 9 – 5n
a3 = 9 – 5 × 3
= 9 – 15
∴ a3 = -6
a1, a2, a3, …………… an
4, -1, -6, …………
d = a2 – a1 = -1 – 4 = -5
d=a3 – a2 = -6 – (-1) = -5
Here, the value of ‘d’ is constant.
∴ an = 9 – 5n form an Arithmetic Progression.
Question 11.
lf the sum of the first n terms of an AP is 4n – n2, what is the first term (that is SI)? What is the sum of first two termš? What is the second term? Similarly. find the 3rdrd the 10th and the nth terms.
Solution:
If Sn = 4n – n2, then
i) S1 = a =?
ii) S2 =?
iii) a2 =?
iv) a3 =?
v) a10 =?
vi) an =?
(i) Sn = 4n – n2
S1 = 4(1) – 12
= 4 – 1
S1 = 3
∴ S1 = a = 3.
(ii) S2 = 4n – n2
S2 = 4(2) – 22
= 8 – 4
S2 = 4
∴ S2 = 4
(iii) We have S2 = a1 + a2 = 4
= 3 + a2 = 4
∴ a2 = 4 – 3
∴a2 = 1
(iv) Sn = 4n – n2
S3= 4(3) – 32
= 12 – 9
S3 = 3
a1 + a2 + a3 = 3
3 + 1 + a3 = 3
4 + a3= 3
∴ a3 = 3 – 4
∴ a 3 = -1
(v) d = a3 – a3 = -1 -1 = -2
a10= a + 9d
= 3 + 9(-2)
= 3 – 18
a10= -15
∴ a10 = -15
(vi) an = a + (n – 1)d
= 3 + (n – 1)(-2)
= 3 + 2n + 2
∴ an = 5 – 2n
∴ an = 5 – 2n
Question 12.
Find the sum of the first 40 positive integers divisible by 6.
Solution:
6 + 12 + 18 + 24 + 40 term
Here a = 6, d = 2 – a1 = 12 – 6 = 6
n = 40, S40 =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{40}=\frac{40}{2}[2 \times 6+(40-1) 6]\)
= 20[12 + 39 × 6]
= 20[12 + 234]
= 20 × 246
∴ S40 = 4920.
Question 13.
Find the sum of first 15 multiples of 8,
Solution:
Sum of the first 15 multiples of 8 ?
8 + 16 + 24+ ……… 15 terms.
Here, a = 8, d = a2 – a1= 16 – 8 = 8
n = 15, S15 =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{15}=\frac{15}{2}[2 \times 8+(15-1) 8]\)
\(=\frac{15}{2}[16+14 \times 8]\)
\(=\frac{15}{2}[16+112]\)
\(=\frac{15}{2} \times 128\)
= 15 × 64
∴ S15 = 960
Question 14.
Fnd the sum of the odd numbers between 0 and 50.
Solution:
Odd numbers between 0 and 50 are
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + ……… + 49 =?
Here. a = 1, d = a3 – a1= 3 – 1 = 2
an = 49, n =?, S =?
an = a + (n – 1) d = 49
= 1 + (n – 1)2 = 49
1 + 2n – 2 = 49
2n – 1 = 49
2n = 49 + 1
2n = 50
\(n=\frac{50}{2}\)
∴ n = 25
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}\left[a+a_{n}\right]\)
\(\mathrm{s}_{25}=\frac{25}{2}[1+49]\)
\(=\frac{25}{2} \times 50\)
= 25 × 25
∴ S25 = 625
Question 15.
A contract on construction job specifies a penalty for delay of completion beyond a certain date as follows: Rs. 200 for the first day. Rs. 250 for the second day. Rs. 300 for the third day. etc.. the penalty for each succeeding day being Rs. 50 more than for the preceeding day. How much money the contractor has to pay as penalty. If he has delayed the work by 30 days?
Solution:
Penalty for the 1st Day 2nd day 3rd day … 30th day
Rs. 200 Rs. 250 Rs. 300 Rs.?
200 + 250 + 300 + 30 days
a = 200, d = 250 – 200 = 50, n = 20,
S30 =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(\dot{\mathrm{S}}_{30}=\frac{30}{2}[2 \times 200+(30-1) 50]\)
= 15[400 + 29 × 50]
= 15 [400 + 1450]
= 15 × 1850
∴ S30= Rs. 27750.
Question 16.
A sum of Rs. 700 is to be used to give seven cash prizes to students of a school for thler overall academic performance. If each prize is Rs. 20 less than its preceding prize, find the value of each of the prizes.
Solution:
Let the first prize be ‘a’.
and Second prize is a – 20 and
the third prize Is a 40.
a, (a – 20), (a – 40) ……….. n = 7
a = a, d = a2 – a1 = a – 20 – a d = -20
n = 7, S7 =?
\(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}[2 \mathrm{a}+(\mathrm{n}-1) \mathrm{d}]=\mathrm{Sn}\)
\(\frac{7}{2}[2 \times a+(7-1)(-20)]=700\)
\(\frac{7}{2}[2 a+6(-20)]=700\)
\(\frac{7}{2}[2 a-120]=700\)
\(2 a-120=700 \times \frac{2}{7}\)
2a – 120 = 200
∴ 2a = 200 + 120
2a = 320
\(\quad a=\frac{320}{2}=R s .160\)
∴ Each prizes are
Rs. 160, 140, 120, 100, 80, 60, 40
Question 17.
In a school, students thought of planting trees in and around the school to reduce air pollution. It was decided that the number of trees, that each section of each class will plant. will be the same as the class. In which they are studying. e.g., a section of Class I will plant 1 tree. a section of Class Il will plant 2 trees and so on till Class XII. There are three sections of each class. How many trees will be planted by the students?
Solution:

a = 3. d = 6 – 3 = 3, n = 12, S12 =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(\mathrm{S}_{12}=\frac{12}{2}[2 \times 3+(12-1) 3]\)
= 6[6 + 11 × 3]
= 6[6 + 33]
= 6 × 39
∴ S12 = 234
∴ Total number of trees from 3 sections of each class upto 12 class is 234.
Question 18.
A spiral is made up of successive semicircles, with centres alternately at A and B, starting with centre at A, of radii 0.5 cm. 1.0 cm. 1.5 cm, 2.0 cm as shows In fig. What Is the total length of such a spiral made up of thirteen consecutive semicircles? (Take \(\pi=\frac{22}{7}\))

[Hint: Length of successive semicircles is l1, l2, l3, l4 with centres at A, B, A. B respectively.]
Solution :
\(: l_{1}=\pi \times \frac{1}{2}, 12=\pi \times 1.13=\pi \times \frac{3}{2}\)
\(l_{1}=\frac{\pi}{2}, \quad l_{2}=\mathrm{p}, \quad l_{3}=\frac{3}{2} \pi\)
∴ Arithmetic Progression,
l1, l2, l3, l4, ………..

Question 19.
200 logs are stacked In the following manner. 20 logs in the bottom row, 19 in the next row, 18 in the row next to it and so on (see the fig. given below). In how many rows are the 200 logs placed and how many logs are In the top row?

Solution:
20, 19, 18, …..
a = 20, d = 19 – 20 = -1
Sn = 200, n =?, an =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(200=\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}[2 \times 20+(\mathrm{n}-1)(-1)]\)
\(200=\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}[40-\mathrm{n}+1]\)
\(200=\frac{n}{2}[41-n]\)
∴ 400 = n(41 – n)
400 = 4n – n2
∴ n2 – 41n + 400 = 0
n2 – 25n – 16n + 400 = 0
n(n – 25) – 16(n – 25) = 0
(n – 25) (n – 16) =
1f n – 16 = 0 then, n = 16
∴ an = a + (n – 1) d
a16= 20 + (16 – 1) (-1)
= 20 + 15(-1)
= 20 – 15
∴ a16 = 5
∴ 200 logs are placed In 16 rows and there are 5 logs in the top row.
Question 20.
In a potato race, a bucket is placed at the starting point, which Is 5 m from the first potato. and the other potatoes are placed 3 m apart in a straight line. There are ten potatoes in the line (see fig, given below)

A competitor starts from the bucket, picks up the nearest potato, runs back with it, drops ¡tin the bucket, runs back to pick up the next potato, runs to the bucket to drop It in, and she continues in the same way until al) the potaotes are in the bucket. What is the total distance the competitor has to run?
(Hint: To pick up the first potato and the second potato, the total distance (in metres) run by a competitor is 2 × 5 +2 × (5 + 3)]
Solution:
Total distance competitor taken to pick up the first potato = 5 + 5m
= 2 × 5m.
= 10m.
Total distance taken by compeUtor to pick up the second potato
= 5 + 3 + 3 + 5m.
= 2 × 5 + 2 × 3
= 2(5 + 3)
= 2 × 8
= 16m.
∴ 10m. 16m, 22m 10th potato
a = 10, d = 16 – 10 = 6m.
n = 10, S10 =?
\(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\)
\(S_{10}=\frac{10}{2}[2 \times 10+(10-1) 6]\)
= 5[20 + 9 × 6]
= 5 [20 + 54]
= 5 × 74
∴ S10 = 370m.
∴ Total distance the competitor has to run to pick up 10 potatoers is 370 m.
Nearest tenth is the first digit after the decimal point.
We hope the given KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 1.3 will help you. If you have any query regarding Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Arithmetic Progressions Exercise 1.3, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.